Content
For example, if the cost of mahogany wood increases by 50 percent, Custom Furniture might renegotiate the price of a mahogany table with the customer. If it’s too late to renegotiate the price of a current job, the cost increase could be built into the pricing of future jobs. When Dan received the company’s income statement for May, he was surprised by the lack of profits. Because sales prices are based on a markup of estimated costs, Dan is questioning the accuracy of his estimates. He approaches Leslie, the full-time accountant for Custom Furniture Company, to get more information.
- Normal costing uses actual direct material and direct labor cost and a predetermined overhead application rate to cost products.
- Calculate the production costs incurred in July for each of the four jobs.
- Measures product costs for a set time period.
- These costs were recorded in an account called G&A expenses.
- $230,000.
An example of an employee time ticket is shown in Exhibit 3.3. When working on a specific job, the employee enters the job number on the time ticket and notes the amount of time spent on that job. When not assigned to a particular job, the employee records the nature of the indirect labour task and the amount a job cost sheet is used to accumulate costs charged to a job. of time spent on the task. At the end of the day, the time tickets are gathered and the Accounting Department enters the direct labour-hours and costs on individual job cost sheets. A job-order cost sheet is prepared for every job; it used to accumulate the manufacturing costs associated with a job.
Why Use A Predetermined Overhead Rate?
A work-in-progress is the cost of unfinished goods in the manufacturing process including labor, raw materials, and overhead. Required Using the step method, allocate the service department costs to the operating departments. In this manner, the other departments will not be required to bear costs for which the service department has already been reimbursed. Issue of direct and indirect materials During April, £52,000 in raw materials were requisitioned from the storeroom for use in production.
There are three reasons for this. Event Forms expects \(\$120,000\) in overhead during the next year. It doesn’t know whether it should apply overhead on the basis of its anticipated direct labor hours of \(6,000\) or its expected machine hours of \(5,000\). What would be the product cost under each predetermined allocation rate if the last job incurred \(\$3,500\) in direct material cost, \(55\) direct labor hours, and \(55\) machine hours? Wages are paid at \(\$17\) per hour.
Job Costing Allocation Of Labor
After all postings have been completed, the sum of the balances in the raw materials subsidiary ledger should equal the a. Balance in the Raw Materials Inventory control account. Cost of materials charged to Work in Process Inventory. Cost of materials purchased. Cost of the materials placed into production. In a job order cost system, each entry to the Work In Process Inventory account should be accompanied by a posting to one or more job cost sheets. Manufacturing companies incorporate job order costing as a means of controlling usage of raw materials, production equipment and labor hours.
When goods are sold, the Cost of Goods Sold account is debited and the Work in Process Inventory account is credited. Factory labor should be assigned to selling and administrative expenses on a proportionate basis. The surest way to price yourself out of a job is to put more emphasis on a potential salary than on how you and the company can help each other. The more your value to a growing company increases, the more you’ll earn. What is the basic form to accumulate the cost of each job under job order costing? Debit to Raw Materials Inventory.
If a department knows it is going to be charged a certain amount for systems design services, regardless of usage, then it is more likely to use the service. We will discuss these issues further in Chapter 19 in the section on shared service centres. Which of the following product situations is better suited to job order costing than to process costing? Each product batch is exactly the same as the prior batch.
Number of personal exemptions claimed by the employee. Job number. A copy of the Online Accounting materials requisition slip a. Is routed to the treasurer’s office for payment.
A job cost sheet is used to accumulate costs charged to a job. The Direct Labor account is’ credited as direct labor is used-that is, as employees work oh specific jobs. A number of mechanical and computerized means have been developed for determining the direct labor cost applicable to each job. At the beginning of the year, Monroe Company estimates annual overhead costs to be $600,000 and that 300,000 machine hours will be operated.
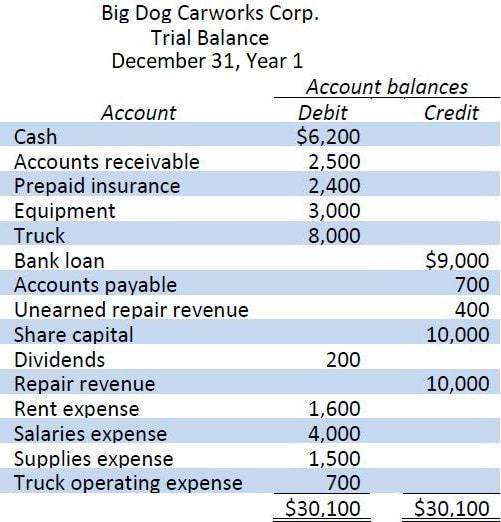
Revenue And Cost Information For Custom Furniture Company
LEARNING OBJECTIVE Exhibit 3.11 presents a schedule of cost of goods manufactured and a schedule of cost of goods sold for Rand Company. The reason for this can be traced back to journal entry and the T-account for Work in Progress that appears in Exhibit 3.10. Under a normal costing system as illustrated in this chapter, applied – not actual – overhead costs are applied to jobs and thus to Work in Progress stock. Note also the cost of goods manufactured for the month (£158,000) agrees with the amount transferred from Work in Progress to Finished Goods for the month as recorded earlier in entry . Also note that this £158,000 figure is used in computing the cost of goods sold for the month.
Overhead is assigned to a job at the rate of $ 2 per machine-hour used on the job. Job 16 had 875 machine-hours so we would charge overhead of $1,750 (850 machine-hours x $2 per machine-hour). Job 17 had 4,050 machine-hours so overhead would be $8,100 (4,050 machine-hours x $2). The journal entry to apply or assign overhead to the jobs would be to move the cost FROM overhead TO work in process inventory. Applied overhead is overhead added to a job by taking the predetermined overhead rate multiplied by theactual activity. Applied overhead is added to direct materials and direct labor to calculate total job cost.
We use Custom Furniture Company as an example throughout the chapter to explain how a job costing system works and to provide information that will address Dan’s concerns. Process Cost System Chapter LO 1 Explain the characteristics and purposes of cost accounting. This information may be required in order to submit the cost information to a customer under a contract where costs are reimbursed. The information is also useful for determining the accuracy of a company’s estimating system, which should be able to quote prices that allow for a reasonable profit.
A profit and loss account for April is presented in Exhibit 3.12. Observe that the cost of goods sold figure on this statement (£123,500) is carried down from Exhibit 3.11. Since actual manufacturing costs are charged to the Manufacturing Overhead control account rather than to Work in Progress, how are manufacturing overhead costs assigned to Work in Progress? The answer is, by means of the predetermined overhead rate. Recall from our discussion LEARNING OBJECTIVE earlier in the chapter that a predetermined overhead rate is established at the beginning of each year. The predetermined overhead rate is then used to apply overhead costs to jobs. When this journal entry is recorded, we also record overhead applied on the appropriate job cost sheet, just as we did with direct materials and direct labor.
Direct labour consists of labour charges that are easily traced to a particular job. Labour charges that cannot easily be traced directly to any job are treated as part of manufacturing overhead. As discussed in Chapter 2, this latter category of labour costs is termed indirect labour and includes tasks such as maintenance, supervision and clean up. Workers use time tickets to record the time they spend on each job and task. A completed time ticket is an hour-by-hour summary of the employee’s activities throughout the day.
Calculate Material Costs
Applied overhead using a predetermined rate of $10 per direct labor hour. Overhead is applied based on a predetermined rate of $12 per machine hour, and 5,100 machine hours were used during June. Prepare a T-account for finished goods inventory and include the beginning balance for March. Post the appropriate items from the journal entries in part b to this account, and calculate the ending balance in finished goods inventory. Prepare a T-account for finished goods inventory and include the beginning balance for September. Post the appropriate items from the journal entries in part a to this account, and calculate the ending balance in finished goods inventory.
Which Companies Use Job Costing?
As such, the difference between WIP and finished goods is based on an inventory’s stage of completion relative to its total inventory. WIP and finished goods refer to the intermediary and final stages of an inventory life cycle, respectively. The difference between WIP and finished goods is based on the inventory’s stage of relative completion, which, in this instance, means saleability. Finished goods refer to the final stage of inventory, in which the product has reached a level of completion where the subsequent stage is the sale to a customer. For example, of the £40,000 ending balance in Work in Progress, £19,500 was overhead that had been applied during the year.
The total costs contained in all job cost sheets for uncompleted jobs should reconcile to the Work in Process Inventory control account balance in the general ledger. Direct material information is gathered from the material requisition forms, while direct labor information is found on employee time sheets or employee labor tickets. Overhead is applied to production using predetermined overhead rates. 114 The gross earnings of factory workers for Dinkel Company during the month of January are $100,000. The employer’s payroll taxes for the factory payroll are $12,000.
Shampoo, scissors, clippers, bowls, towels are indirect materials hence manufacturing Ohs. When a job is completed, its cost is transferred from the work in process account to the finished goods account. After completion, cash flow the job becomes finished goods and is, therefore, transferred from the production department to the finished goods storeroom . First, companies producing individual, unique products known as jobs use job costing .
Actual overhead was less than applied overhead. The predetermined overhead rate is computed using a. Actual overhead costs.
The company allocates service department costs to other departments in the order listed below. Problems of overhead application We need to consider two complications relating to overhead application. These are the computation of underapplied and overapplied overhead and the disposition of any balance remaining in the Manufacturing Overhead account at the end of a period. Since the amounts in entries to all go directly into expense accounts, they will have no effect on the costing of Rand Company’s production for April. Factory overhead was charged to Job C15 at the rate of \(200\%\) direct labor. Prepare the journal entry to eliminate the under- or overapplied overhead. Factory overhead was charged to Job C15 at the rate of \(200\%\) of direct labor.
Regular hours. In a job costing environment, non-direct costs are accumulated into one or more overhead cost pools, from which you allocate costs to open jobs based upon some measure of online bookkeeping cost usage. The key issues when applying overhead are to consistently charge the same types of costs to overhead in all reporting periods and to consistently apply these costs to jobs.
Assume indirect labor costs and utilities will be paid next month. Manufacturing Overhead Allocation Base and Calculating the Cost of Jobs. Elko Company expects to incur $800,000 in manufacturing overhead costs this year.
Provide the account name commonly used by service companies for each of the following accounts used in a manufacturing environment. Describe the two important factors in selecting an overhead allocation base. Calculate the production costs incurred in May for each of the three jobs. Use a job costing system to track costs and evaluate profitability for each job. Recording the application of overhead costs to a job is further illustrated in the T-accounts that follow. A costing system used by companies that produce identical units of product in batches employing a consistent process.
Typically, to calculate the amount of partially completed products in WIP, they are calculated as the percentage of the total overhead, labor, and material costs incurred by the company. A construction company, for example, may bill a company based on various stages of the project, where it may bill when it is 25% or 50% completed, and so forth. Required 1 Identify reasons for entries to . 2 Assume that the company closes any balance in the Manufacturing Overhead account directly to Cost of Goods Sold. Prepare the necessary journal entry. 3 Assume instead that the company allocates any balance in the Manufacturing Overhead account to the other accounts in proportion to the overhead applied in their ending balances. Prepare the necessary journal entry, with supporting computations.